These are some thoughts captured and co-written by Stephen Danelutti and Jason Noble, two long time contributors to the world of Everything As a Service (XaaS) who met again recently. We realised our common background and insights and decided to produce this combined thought piece – hope you enjoy.
Background
We worked at Sony together many years back and only discovered this recently when we met. Funny how our orbits work as people, and then you collide.
We worked in different parts of a division at Sony called DADC, which invented the CD and developed digital content streaming services. This was before iPod, iPhone and Spotify. Stephen has written about that, including a demo: The end of ownership and the rise of usership. This experience was a good precursor to our thinking on Everything as a Service (XaaS).
We met when we both were (and still are) professionally in Customer Success management leadership roles, a function of SaaS companies that is, amongst others, being translated into XaaS. So we are both rather well positioned to talk on this topic.
Stephen is writing an eBook on the subject which you can find out more about here. We decided to use that as a framework (The As a Service Iceberg) for exploring our mutual thoughts. While we divided subtopics up between us, we worked collaboratively throughout to edit and progress in tandem and what you read is very much a joint effort.
Everything as a Service (XaaS)
There is a distinction between the purely technological view which is where the term XaaS comes from and the one we refer to in this article. In ours we have jumped from technology to other industries – we have “crossed the chasm”. Essentially we are talking about taking the learnings from the Software as a Service (SaaS) industry and applying it to other industries.
Some examples
SaaS has been around now for a good few years, and we’ve seen other as-a-service philosophies and approaches pop up since – most related to technology (e.g. infrastructure as a service) but there are more and more examples now across all industries. Some great ones include:
- Mobility and transport – think of an extension of your Oyster card
- Property – renting plus add-on services and services like airbnb
- Shopping – home delivery pre-prepared meals
- Healthcare – shaving services
- Airlines – yes even some airlines are often monthly subscription
- Digital content – not just music, but now movies, TV, games and books

It’s not just about what is being delivered, but how it is being delivered – and the level of experience offered that takes these examples into the true as-a-service arena.
In times of crisis, like COVID-19, there is a stronger need to justify new technology services and innovations, and many businesses are looking at rapid return on investments as part of it. We will see a continued development of new as-a-service ideas coming over the coming years that have been accelerated by the need to innovate and change.
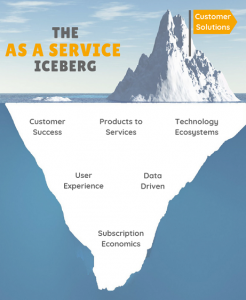
The as a service iceberg
1. Customer solutions
This is the outward manifestation of all of the others and is all about solving problems and meeting needs. No longer is something purchased just for its intrinsic value but what it will help a person or organisation achieve. Several sub components or theories support this and some have been around a while:
- Systems thinking views a system as a cohesive conglomeration of interrelated and interdependent parts and in the case of customer solutions, it represents how products are now increasingly being viewed as tangible goods plus services.
- Business outcomes management entails identifying, measuring and achieving business outcomes for the customer, often with the help of Customer Success teams (see the next influence).
- Jobs to be done theory is a framework for understanding customer needs and innovating around them with new offerings.
- Solution selling is an approach taken by sales teams that incorporates a consultative approach to identifying solutions to best meet a customer’s needs in the most cost efficient way, especially with multiple product offerings.
More elaborated on this in this post: As a Service trend research – customer solutions.
2. Customer success
With the shift to XaaS, the way we interact, work with and deliver to our customers has also evolved. Our customers’ expectations have risen rapidly and we need to focus on what experience they require and want, and also what it is that they are ultimately looking for, in outcome or value terms. The idea from SaaS vendors, that gave rise to customer success, is that they work with customers proactively to drive value and growth for the customer, in turn justifying the vendors offering. The old reactive way was letting the customer figure things out for themselves after the sale. This has been a monumental industry shift and it’s one that is still evolving and maturing. The role of a customer success manager (CSM) is one of the fastest growing roles today as more and more companies understand that it is critical to their own and their customers’ growth and ultimate success.
CSMs are generalists and facilitators, skilled across the business, commercial, technology and product functions. They are uniquely positioned to be able to guide and help customers achieve the outcomes they need, through the (technology) services they acquire. CSM’s act as trusted advisors, facilitators, business and growth consultants, analysts, project and programme managers, even as change managers for their customers.
3. From products to services
This fits alongside the customer solutions view where products play a role in a much wider ecosystem that includes services. It’s not just about technology and technology products, it’s much broader. Having said that, technology does enable this to a far greater degree, see next point. Think about how Apple has taken its iPhone and built an app (and services) ecosystem that serves to add value to Apple hardware and creates new revenue streams for them and third party app developers. These apps are increasingly being sold on a subscription basis which is also interrelated. For the broader context which incorporates service-dominant logic, check out this post: As a Service trend research – products to services.
4. Technology ecosystems
Technology has played a massive part in the shift to as a service. As we’ve seen the rise of technology services over the last 30 years, many more traditional companies (for example content creators and manufacturers) are now working with technology partners, for their technology development and almost outsourcing it. The focus now is about being enabled and empowered to use technology, as opposed to having to own and build it directly. Think of your internal IT department and how that’s changed. They’re now there to help you better utilise technology within the business and integrate with much wider technology ecosystems with external partners.
5. Being data-driven
Collecting data and understanding usage so that it drives greater insight, which in turn drives better products and services, has become a competitive differentiator. Translating this data into meaningful insights is the real challenge that only the leading companies are mastering. Questions like who is using what, how much and to what end, with which outcomes, need answering. You also need to consider where the data is, who can access it and whether this falls within regulatory compliance or not. These are big questions that require a holistic approach. Data science is a growing field that serves this area well and smart as a service companies are investing heavily into building their capabilities in this. A data-driven, decision making culture is also imperative.
6. Customer and user experience
The terms user and customer experience are front and centre now when it comes to technology. This has been driven by the rise of the consumer application ecosystem and high bars being set by companies like Amazon, Netflix and Apple (amongst many others) in how they interact with customers. Customer experience starts from the initial engagement with your customers and potentially through your marketing campaigns and outreaches. It then follows through with onboarding and implementation, project management, delivery, support and more. The challenge is ensuring that you deliver a constant customer experience and that it is specific to that customer (or segment of customers). The key to remember is that not every customer needs, wants or expects the same levels of customer experience.
7. Subscription economics
One of the biggest aspects of the as a service business model is the shift away from one-off payments to recurring payments, or subscription economics. Products and/or services are purchased in this way (on subscription) and sometimes even on an on-demand basis. Especially for B2B firms, this has shifted the financial impact from big capital expenditures upfront (capex) to more manageable on-going operational expenditure over time (opex). Many factors that this model of payment enables, need to be considered. One of the foremost on the vendors side is the emphasis this places on ensuring the customer continues to renew their subscription (not churning) by providing excellent service. For this the customer success managers role is key. Conversely, this makes the model very flexible for customers who can stop payments if they are not receiving any benefit or value. Take a look at this post for some graphics covering other aspects of what makes subscription models successful: Subscription Model Success Factors.
Other examples of where we’re seeing this shift
The shift to as a service as we’ve said started off in the world of technology but we are now seeing it everywhere across all industries. Some great examples include:
- Gaming – all the big players like Sony and Microsoft have game subscription services, and even Google and Apple are now also in this booming market. From our days back at Sony, this way an area that we both were both closely involved with – the digitisation of content and streaming services.
- Groceries – this is one to watch. The big supermarkets all have loyalty plans and they know what we like to buy and when. It won’t be long before this data is used to determine what our weekly grocery deliveries should be and we pay for a subscription service and food is just delivered at the frequency we pay for, and best of all most of what is delivered is exactly what we need.
- Technology – infrastructure as a service, platform as a service and more. With the like of AWS and Azure, we can now “subscribe” to technology services including CPU power and data storage (and the related sub-services) and we can expand or contract our technology operations in response to demand from our own customers (this is all part of the big shift we’ve seen over recent years out to the cloud).
Other considerations
Customer centricity
There’s a lot of talk today about organisations making moves to be more customer centric and it’s something we have spoken and written about many times before (see link here to previous blogs). It boils down to really understanding your customers, as an organisation and being able to be agile and responsive to change as your customers’ needs and requirements change.

From a previous talk Jason did with a firm of VCs, the reason being customer centric is important is not only the obvious – that your customers stay loyal when they have good experiences – but also as our customers keep evolving and changing, so too are the ways that we operationalise that and support those customers.
A great way to think about customer centricity that really resonates with us is – “A business is customer centric when it delivers on-going growing value to and for their customers.”
Business transformation
Becoming an as a service business is not something you can easily tack on, like a plaster. That’s because of the overarching reach of so many of the factors listed above that are required for success. So wholesale transformation is often required for long term success. That doesn’t mean you have to do it all at once – see diagram for different stages and an approach you could take. This is like a product portfolio view of the transformation and tackles it one stage at a time, eventually rolling up into wholesale organisational transformation.
Keep an eye out for more joint blog posts we’ll be working on in the future.